- K -

Andreas
Kammermeier
of Altenbuch (Lower Bavaria, Germany) was a clergyman (
Benefiziat). He was
granted in 1938 a patent (no. 1,427,777*) for an invention that he
called in German
Kartenwinkelmessgerät
i.e. map angle reader. It is supposed to be a
protractor or romer scale
but it is rather a simple tool designed to copy the angles measured
either with it on a map and a red thread (
not shown in the original patent
fig.)
attached to its centre or with a marching compass while observing the
landscape. His argument was that there was no tool for this purpose and
that the foldable ruler of the
BUSCH
compass type which was issued to all army troops (Wehrmacht)
and members of Nazi organisations like NSKK (
Nationalsozialistisches
Kraftfahrkorps),
SA, HJ etc. and featured the counter clockwise 6400 MILS
divisions. This idea was obviously not shared by BUSCH who had
its
own protractor.
The patent is six pages long and very far from a typical patent
wording. The tool's function reminds of the
KRÖPLIN
models so that we suppose that the author may have been a leader of the
"
Wandervögel"
and was nostalgic of this technical solution.
*
NOTE:
In the German patents data base DEPATIS it is listed with the ending
"U" i.e. Registered Trade Mark. The same no. with the ending A is now a
patent issued in 1965 for a machine used to separate tiles. We
presume that the patent was downgraded at about this date and the no.
reallocated.
Click on pic.
at r. for an enlarged view together with the patent's page 1
Swiss company located in Aarau (more
information
HERE).
See also Survey Compasses.

Design Office
drawing
(Click on the images for enlarged views)
|

|
Model
designation BUSSOLE (i.e. compass)
Technical
Data:
 - Dimensions: 73 x 65 x 19
mm, Weight: 162 gr
- Dimensions: 73 x 65 x 19
mm, Weight: 162 gr
- Divisions: 6400 mils clockwise (Swiss Army),
- Fluid damping of needle, luminous paint markings, no
device for adapting to changed magnetic
declination. The
needle seems to be red (link
to pic.) and features the same markings as the bars on
either side.
- Scale (on casing side): 1:50.000 (6 km)
- Production year: 1941 (see drawing)
|
Compass model in use within the Polish Army (Wojsko Polskie, W.P.) and
probably developed on the basis of the French
Modèle
1922.
The letters K and M stand for the inventor's initials, Colonel Mikołaj
Kulwieć, born March 24, 1890. It is also known in Poland as the
„Kulwieć compass“.
Kulwieć had spent some time in France as a member of a military
mission, which maybe explains why his compass ressembles so much the
French Modèle 1922.
It was first produced by
G.
GERLACH (S/No. 0001 to approx.
9000, the first 4000 being
marked
M.K.
32)
and later by
Z.
JEZNACKI
(until
S/No. 20,000?). The initials were probably interverted because of a
possible confusion with the German designation
Marsch-Kompass.
A user's instruction was added only from 1938 on (
Busola
kierunkowa
wzór K.M. Opis i uźycie,
marching compass K.M.,
description and use).
Its advantages were its large diameter and simplicity of utilisation.
Drawbacks were the lack of degrees divisions (it features only mils)
and its heavy weight (200 gr). For comparison: a Bézard
large model weighed only 160 gr. Solely the British Mk III compass was
heavier : 260 grs, example :
T.
G.
Co. Ltd. London.
(
Cited after the Fundacja
Kosciuszki's website - see LINKS).
Instrument
signed by G. GERLACH

Below: the early version M.K. 32: 
(Picture
courtesy
A. Andersen)
|
The
reflecting
characteristics of the GERLACH compass interior surface (see picture
below, left) were much better than the JEZNACKI model (below, right).


(Click
on the picture for enlarged
view) |

Technical Data
- Dimensions: 80 x 72 x 17 mm
- Weight: 200 gr
- Mirror: polished inner surface of metallic lid. It has a sighting
opening made of two partly overlapping circles, so that two convergents
edges form a continuation of the lubber line engraved vertically.
- About the S/N:
* From
S/N 6000 onwards: without the
Army's coat of arms and model designation
See also a pocket
compass with
cardinals in Polish language (go to POLAND).
|
Instrument
signed by Z. JEZNACKI
 |

|
User's
Instructions (1938)


(Click
on the pictures for enlarged
views) |

Ed. KOEHN was a Swiss clock maker.
The
Internet Compass Museum
doesn't possess any other data concerning this company. Your help is
needed.
Ed. KOEHN built a
Verner's
pattern compass called
Mk
VII
(see exhibit made by
French
Limited, F-L, for a Verner's
pattern Mk VIII compass).
A facsimile of the original User
Instructions can
be ordered. (Click
HERE to see a
photograph of page one).
Picture at
right: advertisement in the
French original issue of P. Dériaz' manual Guide
de poche pour l'emploi de la boussole sur terre
published in
1917. It was translated into English and adapted under the title The
prismatic compass and how to use it
(see Prismatic
compasses).
Click on the picture for an enlarged view.

(Click
on pictures for
enlarged view) |
 |
 |
Technical
Data
- Diameter: 54 mm
- Depth: 21 mm
- Weight: 150 gr
- Card material: mother-of-pearl
- Date: 1915

The compass card must be locked by hand. |
Max KOHL AG (Adorferstr. 20 in Chemnitz) was a German company
established 1908. It produced mainly instruments for schools and
universities laboratories as well as measuring equipment for fabric
manufacturers (notice issued by the Leipzig stock exchange). Its code
during WW II was "hap".
 |

Wehrmacht marching compass
(Click
on the pictures for
an enlarged view) |
Technical
Data
- Diameter: 54 mm
- Depth: 17 mm
- Weight: 60 g
- Case: Nickel
- Lid: Aluminium with "broad nose" (s. below) and 4 rivets at the hinge
- Thumb loop: brass
- Ruler: 60 mm, klappbar
NOTE: see lid shape comparison under Breithaupt |

(Click
on the pictures for
an enlarged view) |


Marching compass, WW II |
Technical
Data
- Dimensions: 75 x 55 x 20 mm
- Weight: 80 g
- Case: Bakelite
- Side ruler: 50 mm |

Export catalogue (c. 1920-1930) |

The Chemnitz plant |

A Max KOHL AG share (1940)
(Picture
courtesy Benecke
& Rehse) |
K&R
is a German company
(more information
HERE).
They produce the same high quality compasses than WILKIE whose
patents were taken over in 2005 and supply important retailers like
Eschenbach.
See
also Survey
compasses.
Former German company. Signed a standard WW2 marching compass
(example: see Busch or Breithaupt). This company was only a bakelite
manufacturer (became later no. 78 of the Materialprüfamt
and still later only
"etl"). The compass parts were
supplied by Busch or Breithaupt and assembled.
German company (for more information click
HERE).
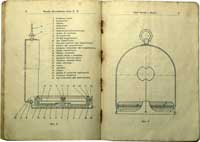
The objective of the patent H. C. Kröplin filed in 1925 (see
KRÖPLIN's prototype of an 'Armeekompass' and his patent in the
category Pocket Compasses) was to make it possible to set a marching
course on a compass without having to orientate a map or even on a
vertical wall map and to transfer this information into the compass. He
designed for this purpose a card with cardinal points and a (red)
pointer that could be inserted under the transparent compass capsule.
This model was built in a small quantity and provided to a hikers'
organisation called
Wandervögel
(migratory birds). This association had
been created in 1901 but ceased to exist after the Nazis
took over power in 1933.
Model
ORION

(Click
on pictures for
enlarged views)
The pictures shows an improved version of the removable card with all
four cardinal points and a better grid. The original card had only
North and South (West and East are engraved on the cover plate) and the
grid only consisted of 3 lines.
The magnetic declination could be adapted by removing the cover plate
and turning the crystal on which a small arrow is painted so that this
arrow points to the right declination value engraved on then coverplate. |

The 40 mm ruler on the rear face

View folded |
Technical
data
- Dimensions: 55 x 50 x 15 mm
- Weight: 70 gr
- Materials: wooden box in a metallic envelope, protection strap in
leather imitation, course setting card made of celluloid
- Needle locking by means of a lever (front face, left, above the
course setting card)
- Capsule painted with luminous compound
Detailled view of the rear face. It is not clear whether the figure 1
under ORION means that this was a first version or the serial number.
Some compasses bear the only words Gesetzlich
geschützt
(protected by law, i.e. registered TM)
.  |
Military
model
(without designation)
This model features a mirror and a bezel.
 |

.
 |
Technical
Data
- Dimensions: 55 x 50 x 20 mm
- Weight: 87 gr
- Divisions: 6400 Mils counterclockwise
- Sighting: gun type sights
- Ruler: on the right side
 |
Former compass maker located in
Nürnberg (Germany) at the time of WWII (more information
HERE).
The brothers Hugo
and Arno
Kührt were granted a patent in 1939 for the use of a
transparent plate with a grid in the compass. The KÜHRT
compass
model was built
by PASTO after WW II but somewhat
smaller. The Online Compass Museum knows only of two similar
compasses built by
KÜHRT. The respective markings on the lid were:
"Kührt DRP" on the large one and "Kührt II DRP" on
the smaller one.
 |

 |
Hugo
and Arno Kührt's
patent no. 682777 (1939)

Technical Data
-
Case: bakelite
- Dimensions: 90 x 77 x 18 mm
- Ruler: 70 mm
- Weight: 115 g
- Divisions inner scale: 6400 mils, counterclockwise
- Divisions outer scale: 360 degrees, clockwise |

(Click
on pictures for
enlarged views)
|
 |
Model
Kührt II
Technical Data
- Case material: bakelite
- Dimensions: 80 x 50 x 18 mm
- Ruler: 70 mm
- Weight: 80 g
- Divisions inner scale: 6400 mils, counter-clockwise
- Divisions outer scale: 360 degrees, clockwise
User's instruction (copy available - German):

|
Polish officer who developed the compass type M.K.32 (or
K.M.32). For more information about Mikołaj Kulwieć, click
HERE
klicken.
- L -
Italian company located in Pomazio belonging to the group of suppliers
of military material called
POLANTEO (link to the Italian website Officina
Radiotelegrafica ed Elettrotecnica del Genio Militare). This instrument
is based on a British MkIII (Barker)
compass,
with some variations, notably the card, the sighting hole on the lid,
and the bezel.

Pictures
by
courtesy of D. Donnini
Click
on pictures for enlarged views |

|

Side view: The filling plug is located on the side!
|
Technical Data
see Barker MK III
S.M.M.E.P is the abbreviation of Stabilimento Militare Materiali Elettronici e di
Precisione, i.e. the department
of the Ministry of
Defense responsible for the supply of military electronic and precision
material. See below
 |
Sidney Solomon Lawrence
was an optician active 67-69 Chancery Lane in London.
He created together with another London optician called Mayo
the company Lawrence
&
Mayo (19 New Oxford Street,
more details HERE).
Some instruments
signed L. & M. were in reality made by famous makers
like F. BARKER, STANLEY or STEWARD (link to example). He filed in
1907 two patents (see table below, photocopies available).
Description (excerpt): "The
back of
the case is
made of transparent material coated on the inside with luminous paint
and sufficiently rough on the outside to enable notes to be written
thereon" (read more in the
original Patent, pic. below).
- Patent no. 10,522 describes a compass with a cylindrical glass card.
The scale is printed on the rim and can be read via a side lense (this
system was also implemented on the models GKS
and Wilkie
110 P).
- Patent no. 24,792 describes a compass with a tiny mirror like the
ones built in the models REFLECTOR,
Cruchon & Emons or
PLAN
Ltd (small concave mirror). The
card's rim is transparent like on the MORDAN
version.
We don't know of any existing compass matching these patents.
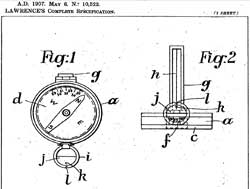
|

(Click
on image above for a view of description - excerpt - page 1)
|
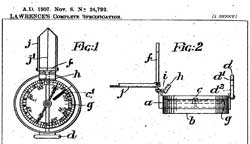
|
Patent 24.792
Read the description in the original
document (excerpt - page 1).
←
Click
on patents images at left for enlarged views of the entire page
|
Major Gilbert LEGH (b. April 21, 1858 - d. Dec. 23. 1939) was
a
British officer (Grenadier Guards) and
inventor. He
designed in 1896 a system making it possible to
read bearings in the darkness wih a precision of one degree (patent no.
19,600 - for figs. click HERE
- complete copy available). The basic principle consisted in placing a
star-shaped metallic stripe with tiny holes upon a
luminous paper disc. The black "star" having 36 branches and
the V-shaped line between two branch ends comprising 10
holes, each hole represents one degree. The loop of the basic
model featured a
sighting
notch. The compass capsule featured a bezel crystal with a radius
painted on it permitting thus to set a bearing.
The prismatic version, signed by Lawrence &
Mayo.,
87
Chancery Lane, London, featured a reticle-shaped sighting vane
in the lid.
This design was also used later on the Magnapole
compass in a simplified version.
 Former French company. The company's name was
later BAILLE-LEMAIRE. It was located 26, rue Oberkampf, Paris 11. It
existed
from ... ? and disappeared approx. about 1980.
It produced like other manufacturers the well-known compass
called Modèle
1922
and
about 10 years after WWII a version of it with a liquid-damped
needle in a transparent capsule called "Mle
22/54" (i.e. 1954) just before it disappeared. The French Army
introduced about at this time the German Bézard
compass. Lemaire also filed in 1953 a patent for an improved system
featuring a hinged hanging mirror like the Swiss RECTA (see BAILLE-LEMAIRE)
called
Model 49 (below).
Former French company. The company's name was
later BAILLE-LEMAIRE. It was located 26, rue Oberkampf, Paris 11. It
existed
from ... ? and disappeared approx. about 1980.
It produced like other manufacturers the well-known compass
called Modèle
1922
and
about 10 years after WWII a version of it with a liquid-damped
needle in a transparent capsule called "Mle
22/54" (i.e. 1954) just before it disappeared. The French Army
introduced about at this time the German Bézard
compass. Lemaire also filed in 1953 a patent for an improved system
featuring a hinged hanging mirror like the Swiss RECTA (see BAILLE-LEMAIRE)
called
Model 49 (below).
It also produced a wrist-top compass (see
this category).
LENDVAY,
Karl
von
Header of the patent no. 108.262
issued in 1926 in Austria but filed in 1925 for Hungary
by Karl von
Lendvay living in Budapest : Instrument
für
die Bestimmung von Entfernungen, Richtungen und Winkeln auf der Karte
und in der Natur
(instrument for measuring distances,
directions and angles on a map and in the field). The compass displayed
below is only one part of the device described in the
patent (see
the eight figures below).

Note that the zero (6400 mils) faces south in conformity with
the
artillery procedures at this time.
Pictures
courtesy J.
Houcke
(click on the images for enlarged views)
|

|
This
instrument was to be
held in 50cm distance from the observer's eye by means of a
lanyard. The rail in the grip held the device shown in the picture at
right (enlarged view) i.e. a rotating plate (fig.
2) with four pairs of points to measure distances on maps with various
scales, a radial (H) divided in Mils to measure angles and
distances on maps. The disc- shaped part features two halves: the top
one being divided in Mils (1600-4800) and the lower one in
degrees
(10°-170°). The concentric circles represent distances
in Mils.
The rectangular windows (C) are used to inscript on the map the
military designation of troops. |
The
complete device
 |
The lensatic compass was invented by F.
Barker
& Son
in 1916
(patent no. 103,019).
Apparently, pre-series models were produced in small
quantities
but the definitive version is the one in the table below at left. The
U.S. ARMY lensatic model was described in W.C. CUDE's patent filed
in 1945.
Lensatic
compasses feature a lens attached to a foldable holder. There are
different holder types: some fold inside the closed compass, other on
top of the lid. The lens holder generally features a (rear)
sight
element,
either a notch or a pin-hole through which the other (fore) sight
element —originally a thin etched line on the cover
window,
later
a metallic wire attached in a slot in the lid— can
be
observed
together with the object being aimed at (compare with prismatic
compass and mirror
compass).
Other lensatic compasses feature a sometimes adjustable lens on the
case side (e.g. Creagh
Osborne, WILKIE Meridian,
unidentified
German military compass, GKS
etc.).
NOTE:
Even the best lensatic compasses cannot compete with the high
precision of a prismatic system (2 deg. vs. one half of one deg. like
with the Barker M-88).

Creagh-Osborne - 1915
(for description go to Creagh-Osborne)
|

F. Barker & Son - 1916
(for description go to DOLLOND)
|

LENSATIC - Basic version (go
to M-1938)
|

M-1938 U.S. ARMY (see CUDE
1945 pat. no. 2,487,044). See also Gurley,
Sup.
Magneto.
|

M-1950
(go to Brunson, Cammenga,
Stocker
& Yale, Lionel Corp., Fee & Stemwedel, Union
Instruments, Miller, Waltham etc.)
|

TRAINING
Pict.
at left: Large-size wooden training device (dia.: 23") probably used
for
demonstration in a training center's classroom (e.g. Camp Lejeune).
(Click on image for
enlarged view).
For training
purposes, the U.S. Army used fold-out guides with a dummy
compass. The black-and-yellow guide doesn't mention any
manufacturer or
production year. The only hint is the verse:
To be "ORIENTED"
you don't
become a JAP*
Simply find your
position on ground and map.
(* Short for Japanese - see
WIKIPEDIA, Pacific
War)
There are more such "good"
jokes like this one: An
AZIMUTH is
not
something you
sit on.
Or this one: Like
ham and eggs your map and your compass go together.
The style of the later version (1968) was much more serious.
See another training (practising) compass in SILVA.


(Click for
enlarged views) |

The
symbols for the cardinal points around the dummy compass are a
polar bear (North), a cowboy (West), a smiling rising sun (East) and a
palmtree (South).
|
Technical
Data
- Dimensions: 4 1/5" x 4 1/2" (110 x 125 mm)
- Number of pages: 6
- Divisions (on dummy compass): 360 deg. clockwise
- Date: 2nd World War
- Conventional signs: general and military
The compass on cover
(pict. left, 1st row, r.) is a
lensatic Model
1938 (see Superior
Magneto
and Gurley).
|


(Click for
enlarged views) |
NOTE
(pic. at left):
"READ RIGHT-UP" compare with the more precise German Planzeiger
system.

This
dummy compass presents all the characteristics of the M-1950
|
Technical
Data
- Dimensions: 6 1/4" X 4 1/4" (159 x 108 mm)
- Number of pages: 6
- Divisions (on dummy compass): 360 deg. and 6400 mils
- Date: 1968 (Vietnam war era)
Excerpt of the footnote on page 6 |
 LEUPOLD is a U.S. manufacturer of optics for rifles (more
information HERE).
LEUPOLD is a U.S. manufacturer of optics for rifles (more
information HERE).
This compass was made by LEUPOLD & STEVENS INSTRUMENTS, INC.
(Portland 13 Oregon). According to
their history (see this company's own website leupold.com), they
built compasses in the 1950's. This item looks at first sight like a
standard forestry
compass (compare with Keuffel
& Esser and LIETZ)
but it additionally features a TOWNSHIP PLAT chart (ref. the cadastral
manual)
inside the cover
which showed the numerical order of sections within a township in
accordance with U.S. Public Lands Survey. This special chart
was already featured on a compass made by
Keuffel & Esser in the 1930's-40's and called RECON. It also
appears on the CRUISER compass model also made by Warren-Knight.
Moreover,
the device
for magnetic declination adjustment was much easier to use. Two basic
models
were proposed: the
smaller SPORTSMAN and the larger and heavier CRUISER*. Moreover,
LEUPOLD proposed a large compass type called FORESTER that
could be fitted onto a staff (model A) and a similar one with
a
graduated sighting vane (model B). This compass occurs with the name of
various manufacturers (LIETZ, GURLEY, CHARVOZ etc. see
Survey Compasses). Some older models were made by Leupold, Volpel &
Co. and
feature user instructions on the face
(pic. clickHERE).
(Pict.
at right:
LEUPOLD ad, late 1950's - click to enlarge)
* Note: Mooers Jr., Robert
L. Finding Your Way In The Outdoors,
Outdoor Life Press (1972), p. 47: The term cruiser compass
derives from the
practice of foresters cruising or estimating the value of a stand of
timber by taking compass readings to ascertain the size of the stand.
(Copies
of catalog, advertisement and manufacturer's manual can be ordered).

(Click
on the images for enlarged views)
The
grid engraved in the lid shows a township
plat. The entire territory of
the U.S.A. has been surveyed by the U.S.G.S.
and divided according to a system of square tracts
measuring 24x24 miles containing each 16 townships
* of 6x6 miles. Each township comprises 36 sections
numbered as shown in the compass grid.
(Cont'd
at right)
|
The two basic models were the
SPORTSMAN
and the
CRUISER* COMPASS
(see
note above)
Markings
were made on ground and they are indicated in the topographical maps
issued by the U.S.G.S. (Quadrangles
or Quads).
This makes orientation for hunters, fishermen and
outdoorsmen
very easy. This system was created for new territories by future
president Th. Jefferson when he was governor of Virginia.
|
SPORTSMAN
- Technical
Data
- Outside diameter: 2 1/2 in.
- Thickness: 1/2 in.
- Weight: 4 oz.
- Needle length: 1 3/4 in.
- Material: Aluminum
- Adjusment of magnetic declination is effected by turning a
slotted pinion gear in the case with a coin or a knife
blade (see pic. below)
 

At r.: Flyer
featuring all L & S compass types (photocopy available)
*
Abbr.: T
= Townships, numbered verticaly,
R = Range, numbered horizontaly, plus initial letter of the
cardinal point.
Read more
details on the website of the U.S.G.S.
We also recommend the booklet CARTERS' Map and Compass
Manual
(150 p.,1954)
|
LIONEL Corp. was U.S. manufacturer (read the full story in
WIKIPEDIA).

(Click
on image
to enlarge)
|
LENSATIC
compass model M-1950
Technical
Data (see Cammenga)
|
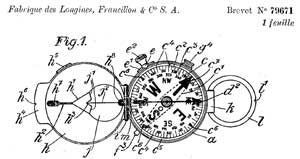 PROFILE
- The company's full name in the early 20th C. was Fabrique des Longines,
Francillon & Co.
S.A. It is located in
St-Imier, Switzerland (read the full
story in
WIKIPEDIA and on this company's website).
PROFILE
- The company's full name in the early 20th C. was Fabrique des Longines,
Francillon & Co.
S.A. It is located in
St-Imier, Switzerland (read the full
story in
WIKIPEDIA and on this company's website).
Longines filed in August 1918 a patent (no. 79671, copy available on request)
describing in all details the famous compass produced by
Plan
Ltd, Cruchon &
Emons.
(compare with the Abercrombie
&
Fitch version).
We suppose that Longines waited until this moment (end of WW1) because
this
instrument was a (secret?) military materiel supplied to the
U.S. Corps of
Engineers.
Drawing:
Longines' patent, figure (click
on the drwg. for a full page view)
 LUFFT is a German manufacturer of barometers (see picture at
right, c.1930's). LUFFT was the manufacturer of the famous BÉZARD
compass. LUFFT also retailed many different pocket compasses
and a diver's
compass
(unknown manufacturer).
LUFFT is a German manufacturer of barometers (see picture at
right, c.1930's). LUFFT was the manufacturer of the famous BÉZARD
compass. LUFFT also retailed many different pocket compasses
and a diver's
compass
(unknown manufacturer).
A.B. (Aktie Bolaget = incorporated company) LYTH is a Swedish
company created in 1861 by Georg
Wilhelm Lyth
(website: www.lyth.se). See also Nautical Compasses. Lyth
manufactured in the 1920's-1930's marching compasses for
Sweden's Army. Lyth cooperated with Björn
Kjellström before
the latter founded SILVA
and several various designs are known bearing both
names after the mention: PATENT S. (= sökt = applied in
Swedish) Mod. KJELLSTRÖM - LYTH. Silva sued
Lyth later because of a patent filed by Lyth in 1931 for a
fluid-dampened marching compass.
Compare with the models built by SILVA and NIFE.

|

|
Modèle
non daté à boîtier en bois avec pour
seul marquage LYTH STOCKHOLM
Fiche
technique
- Dimensions : 70 x 68 x 23 mm
- Divisions : 6300 mill.
- Aiguille sèche
Photos xxx - Cliquer
sur les photos pour les
agrandir
|
Model Lyth 1928, S/N 465
Model with round window
(no date, no S/N)
|
Technical
Data
- Dimensions: 70 x 68 x 23 mm
- Divisions: 6300 mils.
- Dry capsule
All feature a sturdy bakelite case and a massive capsule casing and
bezel.
Click
on images for
enlarged views
|

Picture courtesy
Sihvonen Jarkko
Model with transparent window in the lid with 400 grades division and
40 mm ruler. |
|
 |
Technical
Data
- Dimensions: 70 x 68 x 23mm
- Divisions: 6400 mils.
- Dry capsule, steel mirror in lid
- Ruler: 60mm
- Sighting aids
|
 |
|
Technical Data
- Divisions: 400 grades (read menue / Miscell. / Divisions)
- Markings: STELLA on a five-branches star.
Note the word PATENT but no number. |
CONT'D



 - Dimensions: 73 x 65 x 19
mm, Weight: 162 gr
- Dimensions: 73 x 65 x 19
mm, Weight: 162 gr















 Model ALPIN (current
programme). The prismatic model ALPIN PRO
is used by the Indian
Army
Model ALPIN (current
programme). The prismatic model ALPIN PRO
is used by the Indian
Army







































 PROFILE
- The company's full name in the early 20th C. was Fabrique des Longines,
Francillon & Co.
S.A. It is located in
St-Imier, Switzerland (read the full
story in
WIKIPEDIA and on this company's website).
PROFILE
- The company's full name in the early 20th C. was Fabrique des Longines,
Francillon & Co.
S.A. It is located in
St-Imier, Switzerland (read the full
story in
WIKIPEDIA and on this company's website).
